About US
We are a direct factory for Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), ensuring quality assurance, and support OEM and ODM customization. Welcome to inquire.
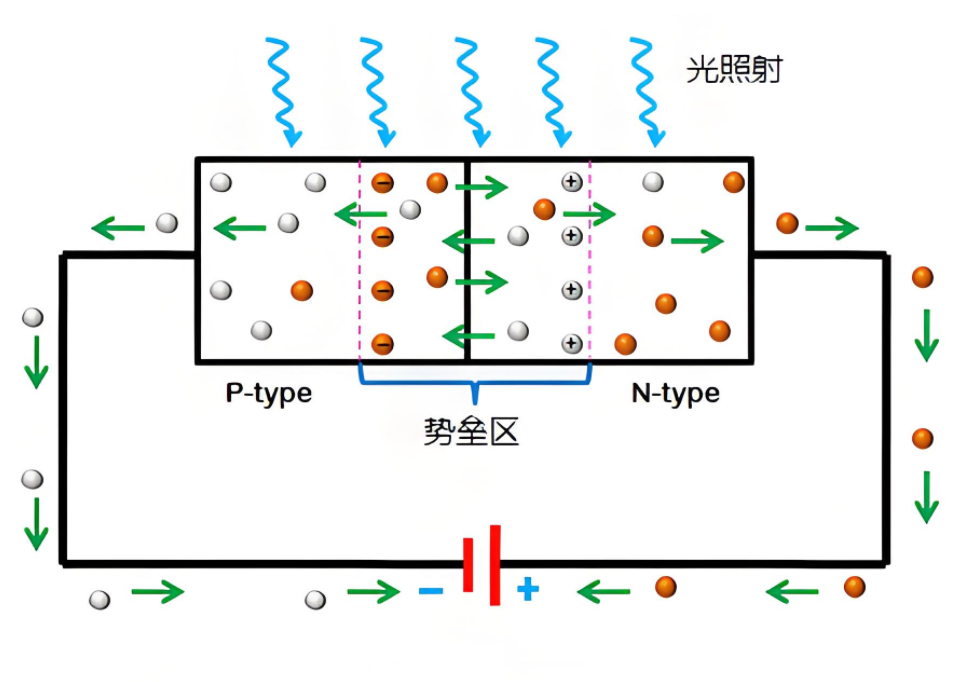
The working principle of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) is based on the electro-optical conversion characteristics of semiconductor materials. The core of an LED is a PN junction, composed of N-type and P-type semiconductors, where the N-type material is rich in electrons and the P-type material is rich in holes. When a forward voltage is applied to the LED, electrons from the N region and holes from the P region meet and recombine near the PN junction, releasing energy in the form of photons, thereby generating visible light.
The color of the light emitted by an LED depends on the type of semiconductor material used. Different semiconductor materials have different energy band gaps, resulting in different photon energies being released, which in turn leads to different wavelengths of emitted light. For example, Gallium Nitride (GaN) material can emit blue light, and by doping with different elements or using different material combinations, LEDs can emit a variety of colors ranging from red to green, yellow, and even white light.
LEDs are highly efficient in converting electrical energy into light energy, which is why they are widely used in lighting, display technology, signal indication, and other fields. Additionally, LEDs have fast response times, are resistant to vibration, and have long service lives.
Leave a comment
All fields marked with an asterisk (*) are required